Large molecules known as Proteins are made up of the building blocks known as amino acids.
- Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, and other elements are found in protein.
- One or more twisted and folded strands of amino acids combine to produce the enormous, complex structures known as protein molecules.
- The most fundamental and significant parts of life actively involved, which are extremely complex molecules.
- These include molecular recognition, cellular communication, mobility, defense, and metabolism.
Classification of Proteins
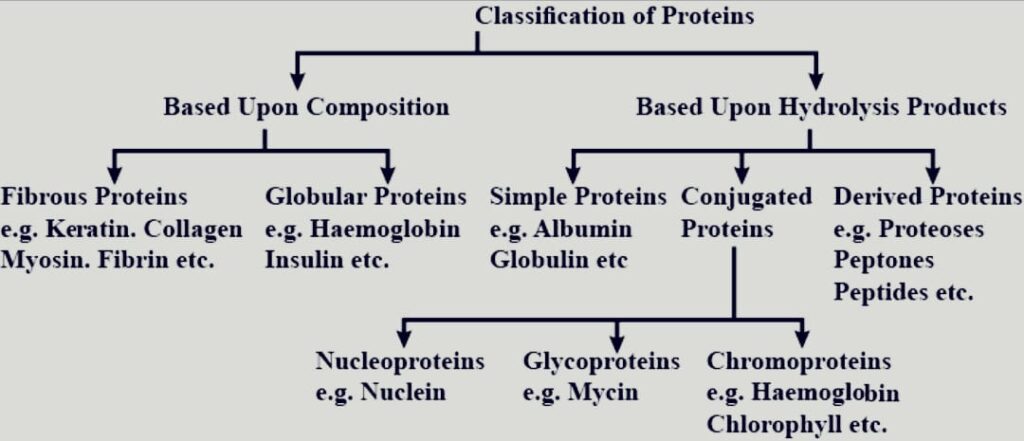
Based Upon Composition
- Fibrous Protein
Animals contain fibrous protein (also known as sclerosoproteins), which are insoluble in water. The protein that make up fibres are coiled, resistant to proteolytic enzymes, and found in threadlike formations. For instance, keratin in hair, claws, feathers, and collagen, actin, and myosin.
2. Globular proteins
Unlike fibrous protein, these proteins are water soluble. Like albumin, insulin, and hormones like oxytocin, they are composed of polypeptides that are wound around themselves to form oval or spherical molecules.
Based Upon Hydrolysis Products
- Simple Protein
They only produce the amino acids and a few rare minor carbohydrate molecules upon hydrolysis. Albumins, globulins, albuminoids, histones, and protamines are a few examples.
2. Conjugated Protein
In the body, simple proteins are mixed with various non-protein substances. Hemoglobin, glycoproteins, phosphoproteins, lecithoproteins, and glycoproteins are a few examples.
3. Derived Protein
These proteins are created by physical or chemical processes from simple or conjugated proteins. Denatured proteins and peptides are two examples.
Proteins Function
- The long amino acid strand develops its highly complex shape as a result of the positive and negative interactions between various atoms.
- Protein that have been folded may come together to form even bigger, more intricate forms.
- A protein’s function in body chemistry is based on how it is folded.
- Natural chemical substances called nucleic acids are the main information-transporting molecules in cells. They are particularly crucial in controlling protein synthesis.
- The shapes of structural protein enable them to construct the fundamental bodily structures.
- Most of the body tissues are held together by collagen, a protein with a fiber-like structure.
- In the skin’s outer layer, keratin, another structural protein, creates a web of waterproof fibers.
- Because of their structures, functional proteins can take part in bodily chemical reactions.
- Some hormones, growth factors, cell membrane receptors, and enzymes are examples of functional protein.
Further Read About:

