Skeletal muscle is a type of muscular tissue that is affixed to the bones and helps various body parts function. As they are controlled by the body’s central nervous system, these muscles are also known as voluntary muscles.
Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
- Skeletal muscle is made up of lengthy, multinucleated muscle cells that are organized into a network of muscular fibres.
- Tendons, which are made up of connective tissues and have a cylindrical shape with branched cells, are elastic tissues or collagen fibres that connect skeletal muscles to the bones.
- Each skeletal muscle contains a tendon at the end that attaches it to the bone and the collagenous layer that covers the outside of the muscle.
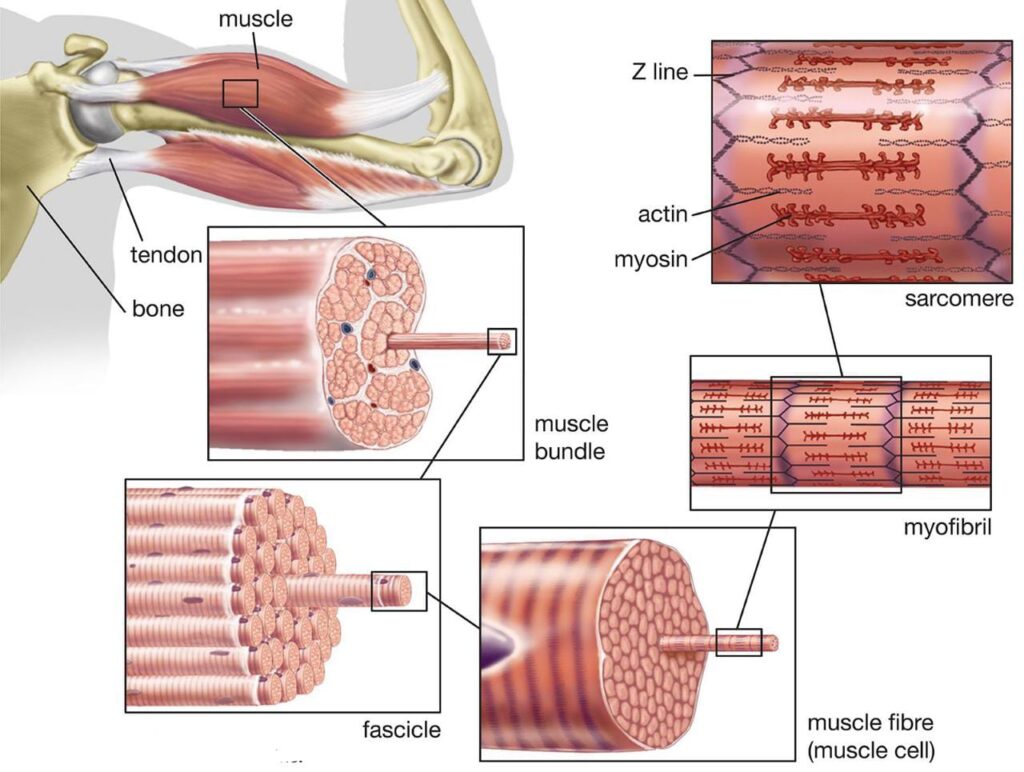
- The fascicles are a collection of muscular fibres that are located beneath the epimysium. Another shield made of collagen surrounds these muscle fibres as protection.
- Blood arteries and nerves can pass through the muscle fibres thanks to the perimysium, a sheath of connective tissue.
Functions of Skeletal Muscle
- It keeps the body’s alignment.
- It controls how hot or cold the body is.
- It is connected to the skeleton and manages its movements.
- It is in charge of carrying out muscle involuntary actions.
- It controls bodily motions including breathing, arm extension, typing, writing, etc.
- It is in charge of the body’s upright posture. The sartorius muscles in the thighs are in charge of movement in the body.
- In addition to offering support to these sensitive organs and tissues, the skeletal muscles shield the interior organs and tissues from any harm.
- These assist the body’s entrance and exit points as well.
Also Read About:

