A state of matter is one of the various configurations that matter can have in chemistry. It has been noted that states of matter can be found in nature in a variety of shapes.
- The matter is composed of incredibly minute particles, which are so microscopic that humans cannot see them with the naked eye.
- Certain materials are hard and have a defined shape, like wood and stone; others that can flow and adopt the shape of their container, like water, and still others that have no set shape or size, like air.
According to their physical characteristics and the states in which they are found, or states of matter, matter can be divided into various groups.
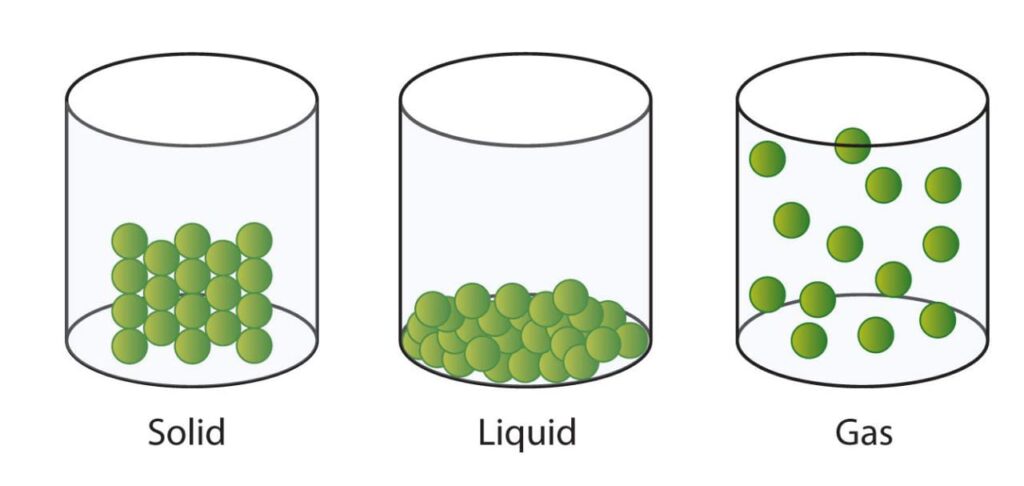
The fundamental states of matter are as follows:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
- Plasma
- Bose-Einstein Condensates
Solid
- Particles are compactly or densely packed in solids.
- Since the spaces between the particles are so small, compression is difficult.
- The volume and shape of a solid are fixed.
- Solid particles can only vibrate about their mean location and cannot move because of its hard nature.
- There is a strong force of attraction between particles.
- In solids, the rate of diffusion is incredibly low.
- Solids include things like ice, sugar, rock, and wood.
Liquid
- Particles are less closely packed in liquids than they are in solids.
- When maintained in a container, liquids adopt that shape.
- Since there is less room for movement between particles in liquids, compression is challenging.
- Although liquids have a fixed volume, their shapes are not.
- Compared to solids, liquids have a higher rate of diffusion.
- Particles exhibit a weaker force of attraction than solids.
- Water, milk, blood, coffee, and other liquids are examples of states of matter.
Gas
- Particles in gases are separated greatly from one another.
- The particles have almost no force of attraction and can move about freely.
- Neither the volume nor the shape of gas is fixed.
- Among solids and liquids, the gaseous state can be compressed the most.
- Diffusion occurs at a faster rate than solids and liquids.
- Compared to solids and liquids, particles have higher kinetic energy.
- Air, helium, nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases are examples of gases.
Other States of Matter
Plasma
- Uncommonly observed form of matter is plasma. Particles with a very high kinetic energy make up the plasma.
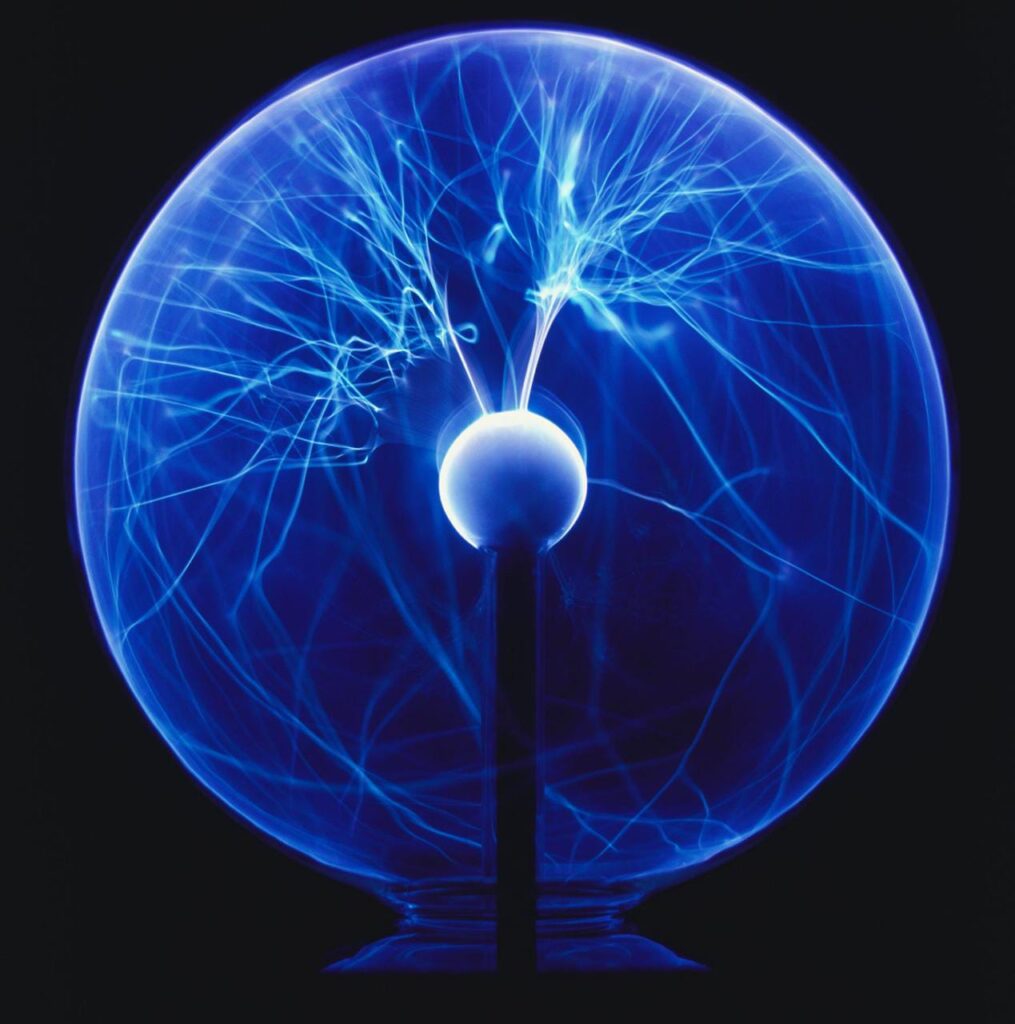

- Noble gases are ionized by electricity to create luminous signs, which are effectively plasma.
- Stars are superheated forms of plasma.
- Lightening, Solar Wind, Nuclear Fireball, and Aurora are examples of plasma.
Bose-Einstein Condensates
- Bose-Einstein condensates were made possible by technological advances and were discovered in 1995.
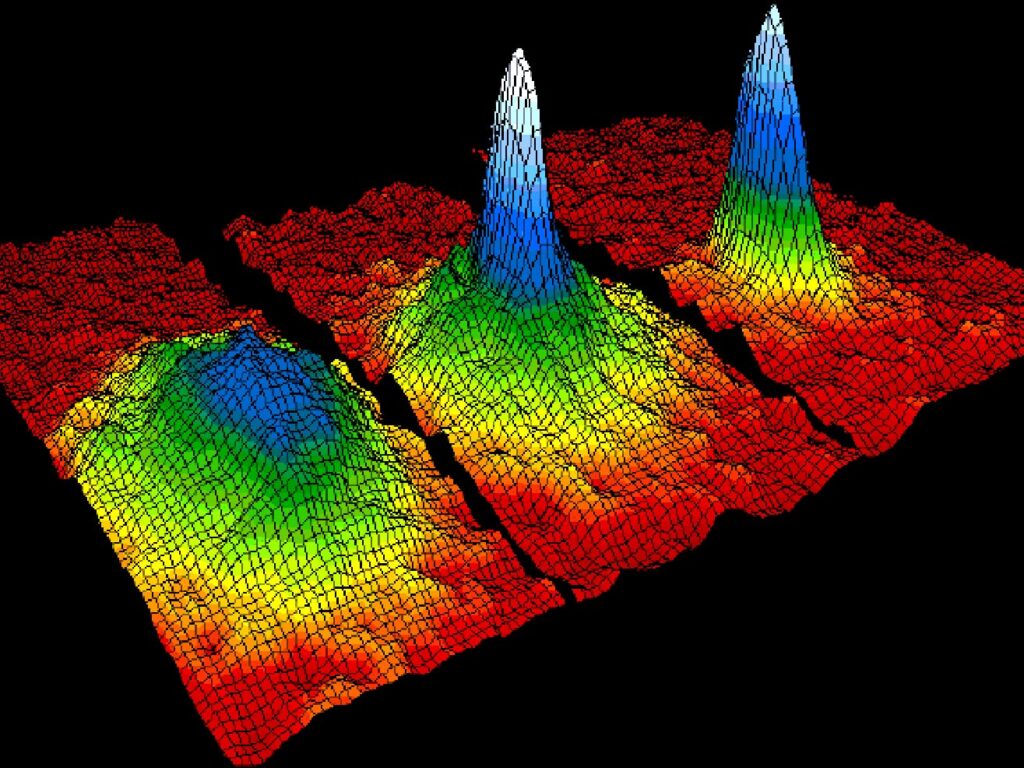
- With the use of magnets and lasers, Carl Weiman and Eric Cornell brought a sample of rubidium to within a few degrees of absolute zero.
- The molecules move very little at the specified temperature. Atoms no longer remain separate as a result of this decrease in kinetic energy; instead, they start to group together. A super-atom is created as the atoms combine.
- As light passes through a BEC, its speed decreases, allowing researchers to learn more about light’s properties as both a wave and particle.
- The qualities of a superfluid are also demonstrated by BECs, indicating that it flows without resistance.
For Further Read:

