Cranial Nerves Mnemonic
The Human brain comprises 12 cranial nerves. It arises from the brain. In these, some of the nerves are sensory, motor, or mixed. Your brain, face, neck, and torso get electrical signals from your cranial nerves. Your cranial nerves aid in the senses of taste, smell, hearing, and touch. They also aid with tongue movement, eye blinking, and facial emotions.
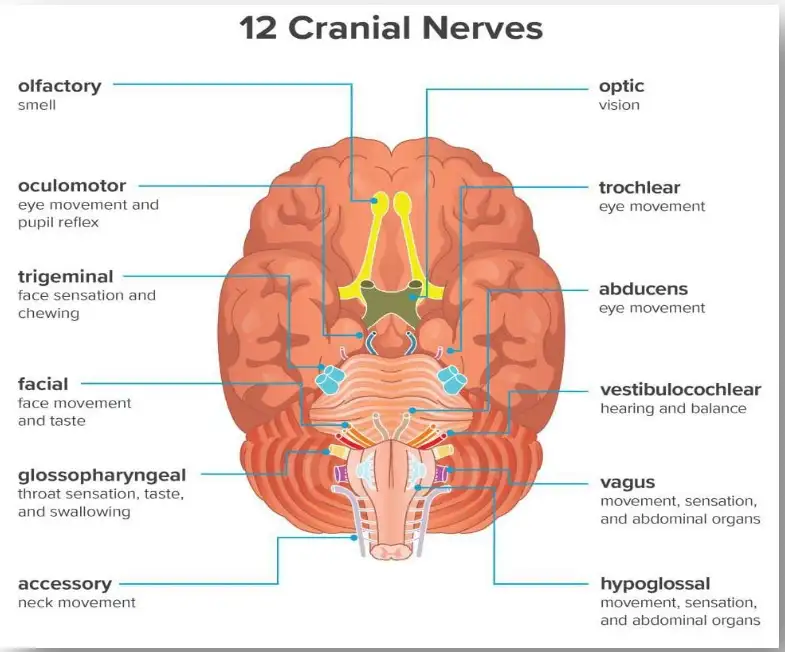
Olfactory CN I
It is the first nerve that is sensory. It is involved in the sense of smell.
Optic Cranial Nerves II
The sensory nerve is involved in vision.
Oculomotor Cranial Nerves III
It is a motor nerve. It has muscle function and pupil response.
Trochlear CN IV
It is a somatic motor nerve, which has command on the superior oblique muscle.
Trigeminal CN V
Largest cranial nerve, which has both sensory and motor function. The trigeminal nerve splits into three branches: ophthalmic (supply to upper part of face), maxillary (supply to middle part of face), and mandibular (supply to lower part of face).
Abducens CN VI
It is a motor nerve that supplies to the lateral rectus muscle. Involved in outward movement of eye.
Facial CN VII
Provides both sensory and motor function. This nerve supplies the muscles of facial expression.
Vestibulocochlear CN VIII
Special sensory nerve which involves hearing and balance.
Glossopharyngeal CN IX
It is a mixed nerve. It provides a sense of taste for the back part of the tongue.
Vagus CN X
The vagus nerve has both sensory and motor functions. It supplies to muscles of pharynx and larynx and sensory supply to external ear.
Spinal Accessory CN XI
It is a motor nerve that supplies to the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
Hypoglossal CN XII
This muscle is involved in the movement of the tongue.
Also Read About:

