Introduction of Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a gut disorder that involves unusually frequent and loose bowel movements. It is a condition in which there is a loss of fluids and electrolytes.
Symptoms
- Loose, watery stools
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Causes of Diarrhea By Viral Infection, Bacterial Infection, and Medication
Viral infection
Norovirus, rotavirus, enteric adenovirus, and cytomegalovirus are the viruses that can cause.
Bacterial infection
Exposure to pathogenic bacteria like E. coli or Campylobacter.
Medication
Many medications, including antibiotics, can cause it. Antibiotics reduce diseases by eliminating harmful bacteria and eradicating beneficial bacteria.
- Eating foods that disturb the digestive system is another potential cause of diarrhea.
- Specific food allergies and intolerances (Celiac disease or lactose intolerance).
- Radiation treatment.
- Food malabsorption (poor absorption).
- Anxiety and tension.
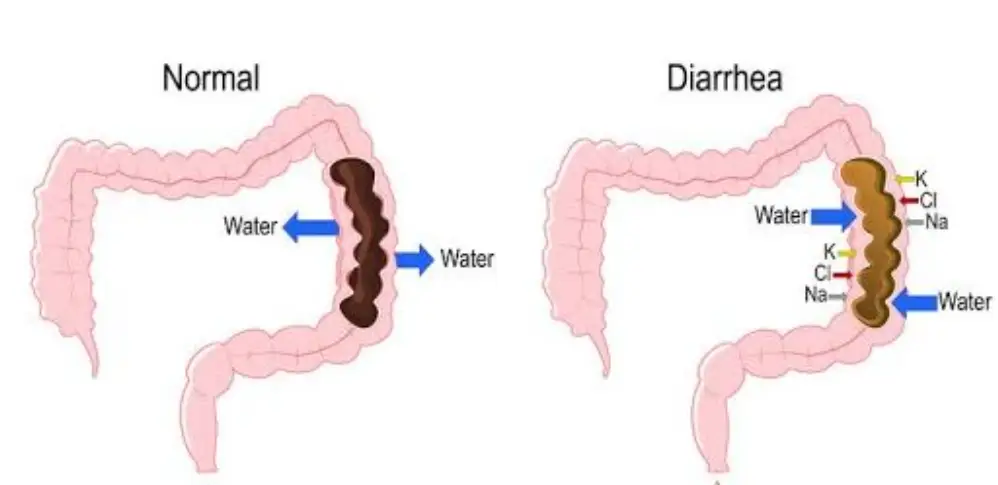
Treatment
- Inadequate water consumption.
- Antibiotics are required if there is a bacterial infection.
Prevention
It can be prevented by;
- Consumption of essential salts
- Taking hygiene measure
- Drinking clean water
- Immunization
Also Read About:

