Common Symptoms of Ulcers
An ulcer refers to any breach in the continuity of the covering epithelium of the skin or mucous membranes. Ulcers are categorized based on etiology, clinical presentation, and pathological basis. Sores that heal slowly or repeatedly recur are known as ulcers. They can take on a variety of shapes and manifest both within and externally in your body.
- They may be visible on parts of your body, like the skin of your leg, or invisible, like the lining of your stomach or upper intestine, as in the case of a peptic ulcer. They can be found almost anywhere on your body, from your eye to your foot.
Etiological Classification
- Traumatic ulcers
- Vascular ulcers
- Neoplastic ulcers
- Inflammatory ulcers
- Infective ulcers
- Ulcers due to malnutrition
Clinical classification
- Spreading ulcers
- Healing ulcers
- Callous ulcers
Pathological classification
- Non-specific ulcers
- specific ulcers
- malignant ulcers
Causes of Ulcer
- Persistent use of Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- H. pylori infection
- Smoking
- Consuming spicy food
- Agitation
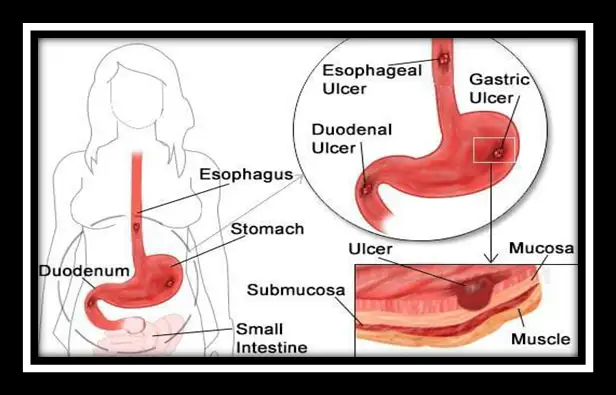
Signs and Symptoms Of Ulcer
The signs and symptoms of ulcers are:
- Abdominal burning after meal
- Nausea
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
Treatment Of Ulcer
Medicines that neutralize the acidic effects are helpful.
Prevention Of Ulcers
- An ulcer caused by an H. pylori infection cannot be prevented.
- By minimizing your use of aspirin and anti-inflammatory medications, you can lower your risks.
- Avoiding orange juice and spicy foods can help ease pain.
- Avoid alcohol and caffeine.
For Further Reading:

