A compound forms when two or more atoms interact chemically.
As an illustration of a compound, the reactions of sodium and chlorine produce sodium chloride (common salt), hydrogen and oxygen produce water, and carbon and oxygen produce carbon dioxide.
Formation of Compound
Chemical bonds are the connecting forces between atoms.
Types of Chemical Bonds
- Ionic Bonds
- Covalent Bonds
- Metallic Bonds
Ionic Bond
- An atom becomes a positively charged ion when it loses or gives away an electron.
- However, when an atom obtains or loses an electron, it transforms into a negatively charged ion.
- When two atoms are in close proximity to one another, one of them gives the other one of its electrons, turning it into a positive ion, while the atom that gets the electron remains a neutral atom.
- Ionic bonds are the electrostatic forces that bind these ions together to create a molecule.
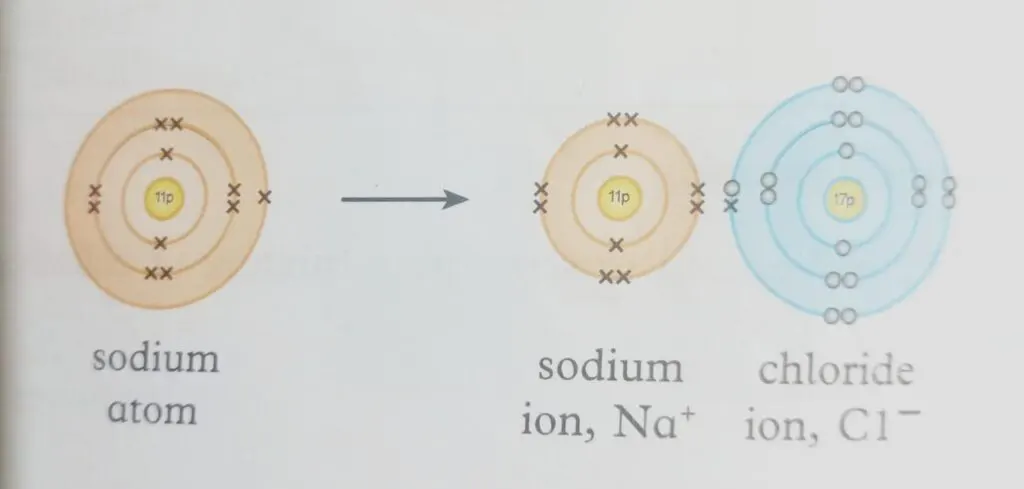
- Take sodium as an example, which has one electron, and chlorine as an example, which has seven electrons in its outermost shell. Chlorine absorbs the electron from the sodium atom, resulting in a positively charged ion.
- After receiving the electron, chlorine transforms into a negatively charged ion. These ions combine to make a compound (sodium chloride), an ionic molecule.
Properties
- They are often solid, hard objects.
- Their melting and boiling points are quite high.
- They typically dissolve in water.
- They are efficient electrical conductors in molten or solution form.
Covalent Compound
- A covalent bond forms when atoms exchange electrons, creating electron pairs.
- When atoms share electrons, a stable equilibrium of the attractive and repulsive forces between them is known as covalent bonding or a stronger bond.
- These electron pairs are also known as shared pairs or bonding pairs.
- Each atom in numerous molecules can reach the equivalent of a full valence shell, thanks to the sharing of electrons, which results in a stable electronic state.
- Covalent bonds are substantially more frequent than ionic bonds in organic chemistry.
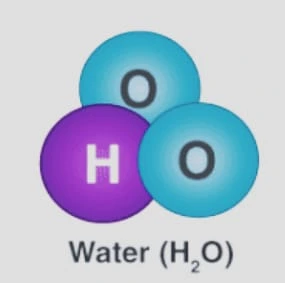
- One oxygen atom, for instance, shares an electron with two hydrogen atoms to create the water molecule.
Properties
- They can be found in solid, liquid, and gaseous forms.
- They are electrically nonconductive.
- Their melting and boiling points are low.
- They are easily evaporated because they are volatile.
- Covalent solvents can dissolve them.
Metallic Bond
- In chemistry, a metallic bond, which is a specific kind of chemical bond made between positively charged atoms, a lattice of cations shares the free electrons.
- Ionic and covalent bonds, on the other hand, develop between two distinct atoms.
- The primary sort of chemical bond that develops between metal atoms is known as metallic bonding.
- Because of the close proximity of the atoms, the electrons of a metal can’t be easily separated from one another.
- Metallic bonds are the kind of bond between the atoms of a metal.
- Copper, iron, and other materials have this kind of connection.
For Further Reading:

