DNA and RNA perform diverse tasks in humans. These are discussed as;
Types Of DNA and RNA
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid)
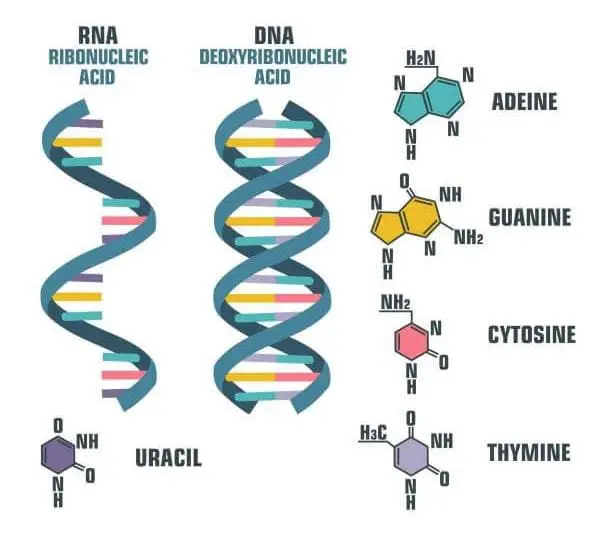
DNA, also known as deoxyribonucleic acid, serves as the initial blueprint for protein production in cells. Deoxyribose, phosphates, and a specific arrangement of the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine are all found in DNA (T).
Types
- A-DNA: It survives in a form that contains 11 nucleotide pairs with an increase of 2.56 vertically per base pair in environments with greater salt concentrations or ionic concentrations, such as K+, Na+, or Cs+, or in a state of dryness. Among all DNA forms, 23 DNA, a typical helix with a right-handed rotation of 32.70 degrees per base pair, has the largest helical diameter.
- B-DNA: The most prevalent type, found in the majority of DNA at physiological salt concentrations and pH neutrality. Per round around the helix axis, there are ten base pairs. The helical diameter is 20, and the distance is 3.4. Watson-Double Crick’s helix model is known as a B-form DNA.
- C-DNA: It is found in the presence of a few ions, such as lithium(Li+), and with a relative humidity of 66%. 9.33 base pairs are present on each turn. The right-handed helix has a diameter of around 19 and a vertical rise for each base pair of 3.320.
- D-DNA: It is an uncommon extreme variant that is observed. With an axial rise of approximately 3.03, the 8 base pairs are inclined negatively from the helix axis.
- Z-DNA: It can be discovered in environments with a lot of salt. It has a left-handed helical structure, in contrast to DNA types A, B, and C. The sugar-phosphate bond forms a zigzag pattern in the backbone, with the dinucleotide serving as the recurrent monomer, unlike the mononucleotide found in alternate forms.
RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid)
A nucleic acid directly involved in the production of proteins is ribonucleic acid (RNA). All living cells contain the significant nucleotide ribonucleic acid, arranged in long chains. Its primary function is to serve as a messenger, carrying DNA’s instructions for regulating protein synthesis.
Ribose, phosphates, and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil are all found in RNA.
DNA and RNA share the nitrogenous bases A, G, and C. Uracil is typically found only in RNA, while thymine is exclusive to DNA.
Types
Only certain cell genes are translated into RNA. Each type of RNA is represented by a specific gene type, as listed below:
- During translation, the transfer RNA (tRNA) transports amino acids to ribosomes.
- The messenger RNA, or mRNA, encodes the polypeptide’s amino acid sequences.
- mRNA is translated into protein-containing organelles called ribosomes by the ribosomal proteins that are produced by the ribosomal RNA, or rRNA.
- Eukaryotes use complexes made of small nuclear RNA (snRNA), proteins, and other building blocks to digest RNA.
Also Read About:

