Soft tissues, including muscles, exist in both humans and animals. Actin and myosin protein filaments make up the muscle cells, which glide past one another to cause contraction and alter the cell’s length and form.
Muscles in humans work by generating force and motion, and they are principally in charge of:
- Movement.
- Changing and maintaining posture.
- The movement of blood cells all over the body.
- Movement of internal organs, such as heartbeat and peristalsis, which moves food through the digestive system.
- More than 600 muscles make up the human muscular system, which accounts for between 40% and 50% of the body’s weight.
- These muscles, which are mostly made up of skeletal muscle, tissue, tendons, and nerves, are connected to our body’s bones, blood vessels, and other internal organs. A type of elastic tissue makes up the muscles in the human muscular system.
- These are primarily fueled by the oxidation of stored energy molecules, such as adenosine triphosphate, as well as lipids and carbs in particular (ATP).
Types of Muscles
Different types are;
- Skeletal or striated muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Smooth muscle
Based on their action into:
- Voluntary muscle
- Involuntary muscle
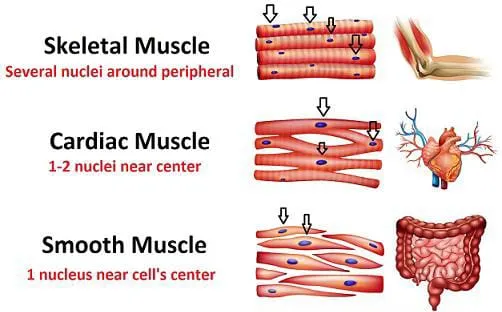
Skeletal Muscle
These muscles are attached to tendons and bones, located beneath the skin layers. They generate movement and are under voluntary control.
Cardiac Muscle
Only the heart contains this muscle. The heart regulates the force of blood pumped throughout the body. It cannot be activated voluntarily.
Smooth Muscle
The walls of the body’s organs, glands, and blood vessels are made of muscle. It is in charge of enlarging and shrinking the way that blood and other fluids move through the organs’ arteries. An uncontrollable muscle is a smooth muscle.
Based on Action:
Voluntary Muscle
Bundles of sarcomeres form long, multinucleated cells that make up voluntary muscle. These muscles typically attach to bones and skin and consist of cylindrical fibers. By contracting and relaxing, they play a significant part in enabling the body to move, and the somatosensory nervous system primarily regulates their functions. Skeletal muscles are a part of these.
lnvoluntary Muscle
The heart muscle serves as an example of a striated, branching involuntary muscle. The body’s autonomic nervous system primarily regulates the actions of involuntary muscles. Smooth and cardiac muscles are some examples.
Also Read About:

