The fundamental building components of matter are described as atoms.
- It is the lowest component of matter that possesses chemical elemental characteristics.
- Atoms don’t exist on their own; instead, they unite to create ions and molecules, which then join together to create the matter that we can see, feel, and touch.
- An atom is the smallest unit of an element, which may or may not be capable of independent existence but always participates in a chemical reaction.
- The smallest component that still possesses an element’s properties is called an atom.
- Subatomic particles, which make up an atom, cannot be created or destroyed.
- The atoms of the same element are identical to one another.
- Atoms are rearranged during chemical reactions.
Size Of an Atom
Atoms have a size that is far smaller than what we can imagine. More than a billion atoms can be stacked together to make an atom layer that is as thick as a thin sheet of paper.
- The position of the electrons surrounding the nucleus makes it impossible to determine the size of an isolated atom.
- However, it is possible to calculate the size of an atom by assuming that the space between neighboring atoms is equal to half of its radius.
- Nanometers are typically used to measure atomic radius.
- An atom can create chemical compounds like molecules or crystals by joining up with one or more other atoms through chemical bonds.
- The majority of the physical changes seen in nature are caused by atoms’ capacity to bind and detach.
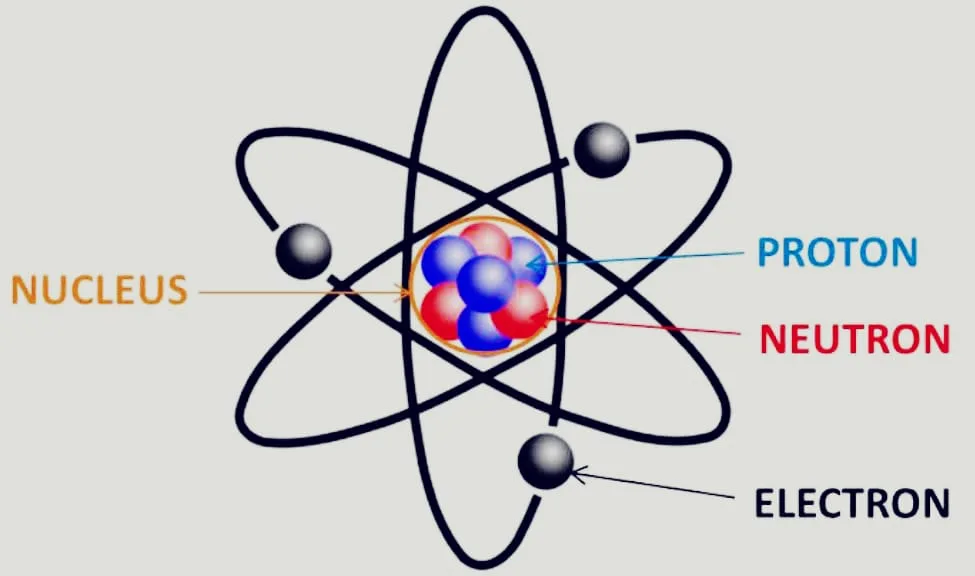
How is an atom created?
- Protons, neutrons, and electrons make up an atom, with hydrogen being the sole exception since it lacks neutrons.
- Every atom has a nucleus, which is surrounded by one or more electrons.
- An atom’s kinetic and potential energy is produced by the motion of its electrons.
- Protons and neutrons, together known as nucleons, normally make up the same number of the nucleus.
- Neutrons are neutral, protons are positively charged, and electrons are negatively charged.
For Further Reading:

