Role of Enzymes in Metabolic Reactions

Enzymes are the Biological catalysts that speed up the reaction and reduce the “Activation Energy”. We have many types of enzymes in our bodies. Some are working with Starch and some with Proteins. Ensure that the rates of Metabolic Reactions are great enough to sustain life. These are very helpful in making the work easier and doing the work in less time with less effort.
Activation Energy: It is the energy that a reactant requires to start a reaction.
Properties
- Lower Down the Activation Energy.
- Made up of Protein.
- Control the reaction.
- Required in small quantities and can be used again and again.
- Enzymes are highly specific.
- They have their own optimum temperature and pH.
Factors
- Temperature
- pH
Catalyst: A substance that increases the rate of a reaction.
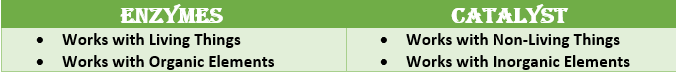
Difference between Catalyst and Enzyme
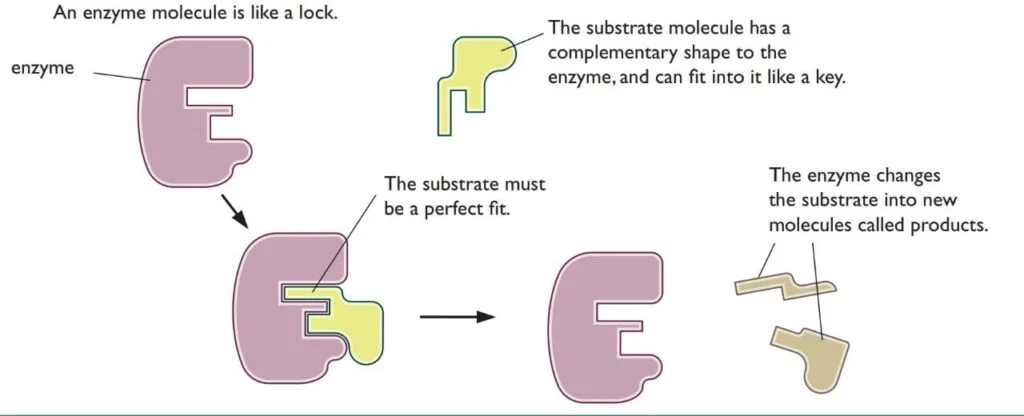
Active Site: This is the place in Enzyme where the substrate binds with the enzyme. Each enzyme has its own Substrate. The substance present at the beginning of the reaction is called the substrate, while the substance produced by the reaction is called the product. The theory called the “Lock and Key Mechanism” helps identify this active site.
Lock and Key Machanism: It tells us about the enzyme’s active site. This theory states that just as every lock has its own key, every enzyme has its own substrate. For instance, the enzyme that breaks down protein is called protease. Protease Enzyme is a lock, and its substrate, which it works with, is protein.
The same is true for other Enzymes: Amylase works with starch, Carbohydrase works with Carbohydrates, etc…
Naming Enzymes: There was a big clash between scientists at the time of the Discovery of Enzymes. A group of scientists had an opinion about naming the Enzyme the same as the Name of the Scientists. After discovering many enzymes, scientists decided to name them based on their substrate and add “ASE” at the end, as each scientist identified numerous enzymes.
Examples of Naming Enzymes
- Protease working on Protein.
- Amylase working on Starch.
- Carbohydrase working on Carbohydrates.

