Cardiac muscles are self-stimulating, only located in the heart, and have a medium rate of contraction and energy requirement.
- The musculoskeletal system does not include this muscle.
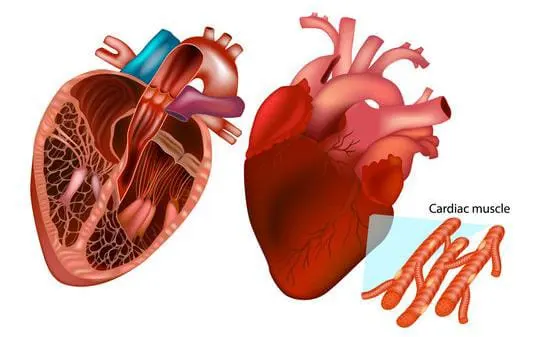
- Striated muscles called cardiac muscles pump and circulate blood throughout the body.
- They carry out involuntary muscular actions to keep our hearts healthy.
- They are constantly contracting and relaxing in sync.
- The heart muscle tissue is strong and flexible because of the connecting muscle cells or fibers.
Structure
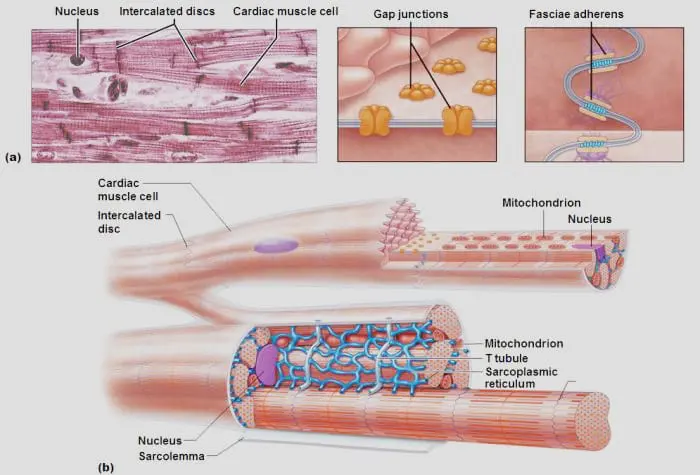
- Each cardiac muscle cell, or cardiomyocyte, consists of a tubular structure with chains of myofibrils.
- Myofibrils are rod-like components present inside the cell.
- Sarcomeres, the primary contractile units of muscle cells, repeat in sections to form the myofibrils.
- Long proteins that form myofilaments, or thick and thin filaments, make up sarcomeres.
- Actin is a protein found in thin myofilaments, and myosin is a protein found in thick myofilaments.
- As the muscle contracts and relaxes, the myofilaments move past one another.
- When an action potential is delivered to the muscle, a mechanism known as excitation-contraction.
- Coupling triggers the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), activating this process.
- The development of “cross-bridges” results from the movement of actin and myosin.
- Heart contractions and energy are produced when actin and myosin move.
Function Of Cardiac Muscles
The main job of the cardiac muscle is to control how the heart beats by contracting and relaxing the heart muscles. Additional jobs performed by cardiac muscles include:
- The cardiac muscles perform the role of an unconscious muscle.
- The act of moving or moving about involves the heart muscles as well.
- The heart’s muscles never stop working, day or night.
- They operate automatically, forcing the heart to compress the blood vessels.
- And then relax them to allow the heart to re-fill with blood.
- A unique form of cardiac tissue made up of “pacemaker” cells makes up the heart. In reaction to electrical signals from the nervous system, they shrink and expand.
Also Read About:

