Cell Organelles and Their Functions
The most essential building block of life is the cell.
- Cells comprise all living things. They could consist of several cells or just one (unicellular) or multicellular).
- Therefore, the lowest autonomous component that we would discover if we dissected an organism down to its cellular level is the cell.
- The tiniest known cells are mycoplasmas.
- The foundation of all living things is cells.
- They give the body structure and transform the food’s nutrients into energy.
- Complex cells have many parts that each serve a different purpose within an organism.
- Similar to constructing bricks, they come in a variety of sizes and shapes. The cells that make up our body come in a variety of sizes and forms.
- The smallest unit of organization in all living things is cells.
- Cell number varies from organism to organism. When compared to microbes, humans have more cells.
- Numerous cell organelles that execute specific tasks to carry out life processes make up cells.
- There is a distinct structure for each organelle.
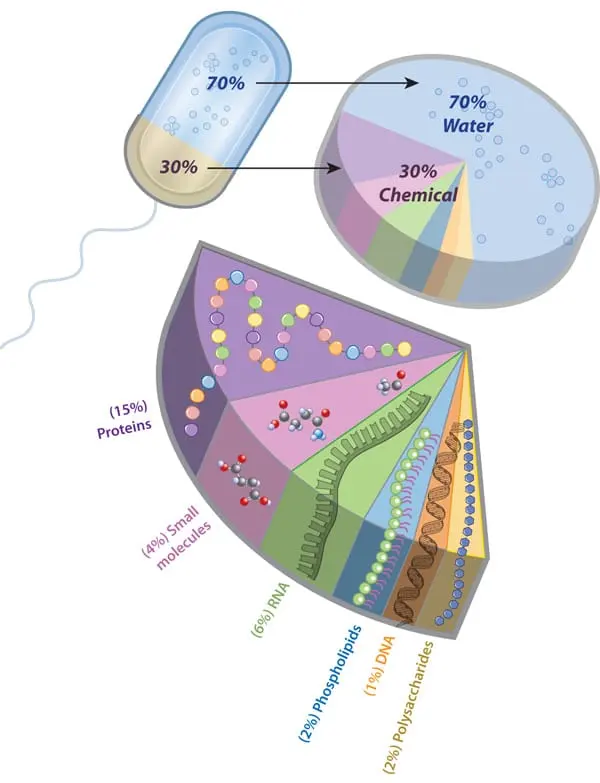
- The cells also contain the genetic material of the organisms.
Who made the first cell?
The cell was found by Robert Hooke in 1665. Under a compound microscope, Robert Hooke examined a piece of bottle cork and detected minute structures that resembled tiny rooms. As a result, he gave these “rooms” the moniker “cells.” However, the restricted magnification of his compound microscope prevented him from seeing any finer features of the structure. This restriction led Hooke to the conclusion that these were non-living things.
Later, utilizing a different compound microscope with higher magnification, Anton Van Leeuwenhoek examined cells. This time, he observed that the cells were moving in some way (motility). Leeuwenhoek concluded that these minuscule objects were “living” as a result. Eventually, following a variety of other findings, these objects were given the term “animalcules.”
Robert Brown, a Scottish botanist, made the first discoveries about the composition of cells in 1883. He was able to explain the nucleus found in orchid cells.
Specifications
The following are some of the key traits of cells:
- Cells support and give structure to an organism’s body.
- The cell’s interior contains many organelles, each surrounded by a distinct membrane.
- The nucleus, a primary organelle, stores the genetic material required for cell growth and reproduction.
- Each cell has a single nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles that are membrane-bounded.
- The primary organelle with two membranes around it, the mitochondria, is in charge of the energy exchanges necessary for the survival of the cell.
- In the cell, waste products are broken down by lysosomes.
- By synthesizing specific molecules and processing, guiding, and sorting them to their proper sites, the endoplasmic reticulum contributes significantly to the internal organization of the cell.
Also Read About:

