Understanding the Cerebrum: Functions and Structure
The cerebrum is the largest and topmost part of the brain. Two-thirds of the weight of the brain is made up of the cerebral hemispheres, which make up the cerebrum. The functionally dominant hemisphere, often the left, governs language and speech. The opposing hemisphere decodes spatial and visual information.
- The inner core of the cerebral hemispheres is made up of myelinated nerve fibers, or white matter, and the outer cortex is made up of gray matter. The cerebral cortex is in charge of coordinating muscular activity, higher intellectual activities, and the integration of sensory inputs.
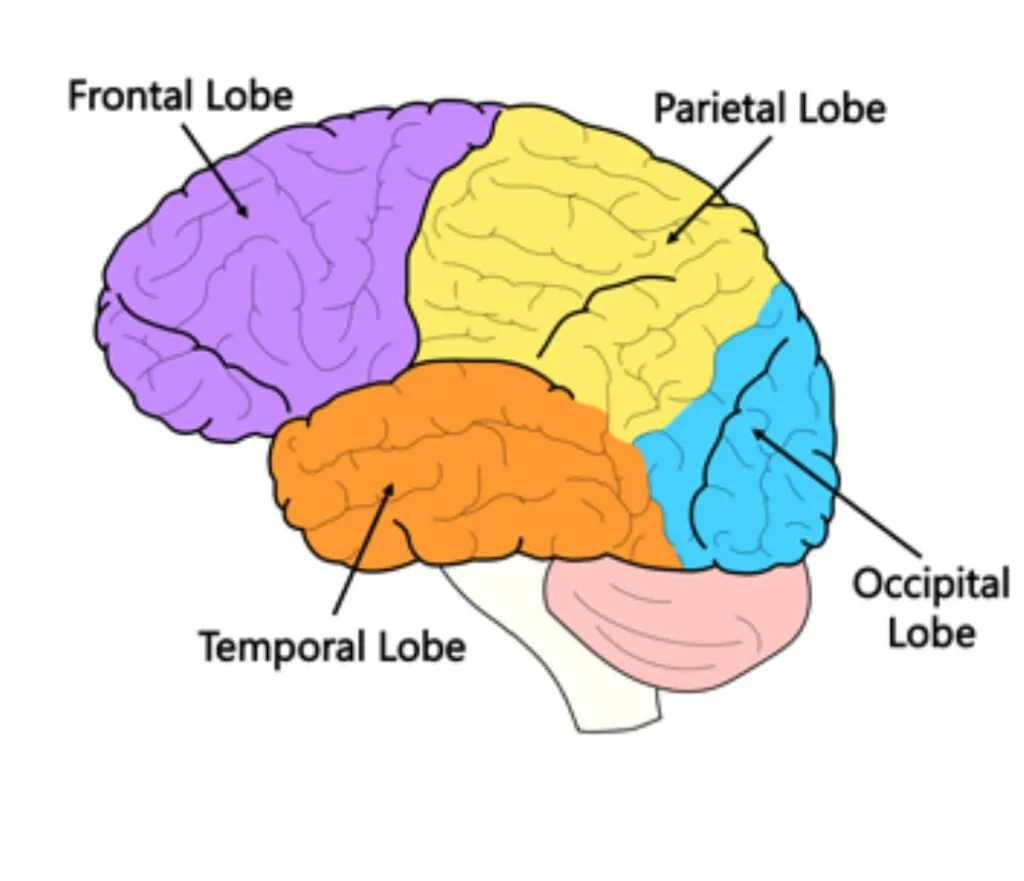
Lobes Of the Cerebrum
The four major lobes are also located within the cerebral cortex.
- The Frontal Lobe
- The Parietal Lobe
- The Occipital Lobe
- The Temporal Lobe
Frontal Lobe:
- The frontal lobes are crucial for controlling higher-order executive functions, expressive language, and voluntary movement.
- Executive functions refer to the ability to plan, organize, initiate, self-monitor, and manage responses to accomplish a goal.
- Our personality resides in the frontal lobes, which function as the control center for emotion and behavior.
Parietal Lobe:
- There are two distinct functional regions in the parietal lobes. In the first, the brain combines sensory data from various senses to create a single perception (also known as cognition).
- The second is integrating sensory information, which is primarily visual and helps us create spatial representations of the environment.
- As we continue to engage with the outside environment, the parietal lobes house a number of separate and ever-updating spatial reference maps of the body.
Occipital Lobe:
- The occipital lobe processes visual information in the brain.
- It plays a role in memory formation, object and face recognition, color perception, depth and distance perception, and visuospatial processing.
Temporal lobe:
- The temporal lobes play a crucial role in processing emotions, language, and certain aspects of visual perception.
- For the majority of people, the dominant temporal lobe is on the left side, and it is responsible for language comprehension, verbal learning, and memory.
For Further Reading:

