Abstract Of KSA NDMO METADATA
Metadata structure (KSA NDMO) plays a crucial role in data governance, as well as data management by providing structured information about data assets. This is also critical for data security, and privacy, as it provides clear visibility, and control over data assets. Metadata helps classify sensitive data, enforce access control, and track lineage. This post explores the development of a metadata structure in alignment with the NDMO – National Data Management Office, Data Catalog Guidelines. It also highlights the key business metadata attributes required for population in the Data Catalog, the augmentation of metadata based on organizational needs, and the strategic considerations for successful implementation.
Keywords KSA NDMO METADATA
Business Metadata; Data Catalog; Data Governance; Metadata Structure; Reference Data; Master Data; NDMO; GDPR; CCPA; PDPL; Risks; Data Security; Data Privacy; Data Protection; Regulation & Compliance; Big Data; Data Quality
Introduction
Metadata is essential for effective data governance, facilitating data discovery, classification, and management. The National Data Management Office (NDMO) provides guidelines to ensure standardized metadata structures within entities. Adhering to these guidelines ensures consistency, improves data interoperability, and enhances decision-making processes. This post discusses the essential components of a metadata structure, including business metadata attributes mandated by NDMO, customization options for organizations, and implementation strategies to optimize metadata utilization.
Understanding Metadata Architecture
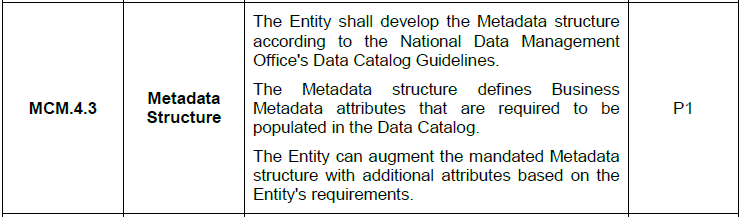
A metadata structure is a standardized way of defining and organizing information about data. The NDMO – National Data Management Office, provides guidelines on how organizations should structure metadata within a Data Catalog. This includes mandatory business metadata attributes that describe the data’s purpose, ownership, classification, and usage. Organizations can expand on this structure by adding additional attributes based on their specific needs. Proper metadata management enhances data accessibility, governance, and compliance.
A well-planned metadata architecture ensures that data is documented, accessible, and properly governed within an organization, improving searchability, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
Examples of Metadata Models
- DAMA-DMBOK Metadata Model – A widely used framework for enterprise data management.
- NDMO Metadata Framework – Designed to align with Saudi Arabia’s data governance standards and ensure compliance.
- ISO/IEC 11179 Metadata Model – A globally recognized standard for metadata registries and classification.
- Metadata Models in Data Warehouses – Includes schema metadata, ETL metadata, and usage statistics to support analytics and reporting.
Key Strategic Points of NDMO
- Aligning metadata structure with NDMO guidelines ensures regulatory compliance.
- Defining mandatory business metadata attributes enhances data cataloging and governance.
- Metadata optimization, and enhancement allows organizations to address specific business needs.
- Standardized metadata improves interoperability and data discoverability.
Potential Use Cases
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring metadata adherence to NDMO guidelines.
- Data Discovery & Accessibility: Facilitating structured access to organizational data.
- Enterprise Data Governance: Enhancing metadata standardization across business units.
- Audit & Risk Management: Enabling metadata-driven traceability and accountability.
- Advanced Analytics & AI: Leveraging metadata for machine learning model development.
General Activation Steps
- Assess Existing Metadata Framework: Identify current metadata practices.
- Map NDMO Guidelines to Internal Metadata Standards: Align existing structures with required standards.
- Define Business Metadata Attributes: Ensure all mandatory attributes (such as data purpose, ownership, classification, etc.) are incorporated.
- Augment Metadata Structure as Needed: Customize additional attributes for business-specific requirements.
- Implement Metadata in Data Catalog: Populate and validate metadata entries.
- Monitor and Improve Metadata Management: Establish governance mechanisms for continuous improvement.
Enablement Methodology
- Governance Model: Define roles and responsibilities for metadata management.
- Training and Awareness: Educate stakeholders on the importance of metadata.
- Technology Enablement: Leverage metadata management tools and automation.
- Integration with Data Strategy: Align metadata initiatives with enterprise data governance policies.
Dependencies & Prerequisites
- NDMO Data Catalog Guidelines: Adherence to national regulatory standards.
- Data Governance Framework: Predefined governance policies and processes.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involvement of data stewards, business users, and IT teams.
- Technology Infrastructure: Availability of metadata management and data cataloging tools.
Tools & Technologies
- Metadata Management Solutions: Collate, Collibra, Informatica, Alation
- Data Cataloging Tools: Open-Metadata, Apache Atlas, AWS Glue Data Catalog
- Automation & Integration: API-based metadata enrichment, AI-driven metadata tagging
- Data Governance Platforms: IBM Data Governance, Talend, Microsoft Purview
Challenges & Risks
- Compliance Complexity: Ensuring complete adherence to evolving regulations.
- Data Quality Issues: Inconsistent or incomplete metadata entries.
- Scalability Concerns: Managing metadata expansion as data assets grow.
- User Adoption Barriers: Resistance to new metadata management processes.
Success Criteria & KPIs
- Metadata Coverage: Percentage of business-critical data assets documented with metadata.
- Compliance Adherence: Alignment of metadata attributes with NDMO requirements.
- Data Catalog Utilization: Number of metadata queries and user interactions.
- Governance Maturity Level: Effectiveness of metadata governance frameworks.
- Operational Efficiency: Reduction in time spent searching for metadata.
Conclusion
Developing and implementing a metadata structure aligned with NDMO’s Data Catalog Guidelines is essential for robust data governance. Organizations must ensure compliance by defining and populating required business metadata attributes while allowing for augmentation to meet specific needs. Strategic activation, enablement methodologies, and the use of appropriate tools and technologies are critical for success. Addressing challenges and monitoring KPIs will ensure continuous improvement and optimal metadata management practices. By following a structured approach, entities can enhance data governance, improve regulatory compliance, and maximize the value of their data assets.

Further Recommended Resources
- Big Data vs. Traditional Data, Data Warehousing, AI, and Beyond
- A Comparative Analysis – OBIEE vs. GA4 vs. Power BI
- Big Data Transformation Across Industries
- Big Data Security, Privacy, and Protection, & Addressing the Challenges of Big Data
- Designing Big Data Infrastructure and Modeling
- Leveraging Big Data through NoSQL Databases
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – Data Governance Principles
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – Compliance Features
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – Data Governance Frameworks
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – Real World Use Cases, and Scenarios
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – General Activation Steps
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – Enablement Methodology
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – Challenges & Risks in BDaaS Implementation
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – Shared Responsibility Model
- BDaaS (Big Data As-a-Service) – Continuous Improvement Cycle
- Data Strategy vs. Data Platform Strategy
- ABAC – Attribute-Based Access Control
- Consequences of Personal Data Breaches
- Key Prerequisites for Successful KSA PDPL Implementation
- KSA PDPL (Personal Data Protection Law) – Initial Framework
- KSA PDPL – Consent Not Mandatory
- KSA PDPL Article 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, & 12
- KSA PDPL Article 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, & 31
- KSA NDMO – Data Catalog and Metadata
- KSA NDMO – Data Catalog and Metadata – Data Catalog Plan – MCM.1.1 P1
- KSA NDMO – Data Catalog and Metadata – Metadata Architecture – MCM.1.3 P1
- KSA NDMO – Personal Data Protection – Initial Assessment
- KSA NDMO – DG Artifacts Control – Data Management Issue Tracking Register
- KSA NDMO – Personal Data Protection – PDP Plan, & PDP Training, Data Breach Notification
- KSA NDMO – Classification Process, Data Breach Management, & Data Subject Rights
- KSA NDMO – Privacy Notice and Consent Management
- Enterprise Architecture Governance & TOGAF – Components
- Enterprise Architecture & Architecture Framework
- TOGAF – ADM (Architecture Development Method) vs. Enterprise Continuum
- TOGAF – Architecture Content Framework
- TOGAF – ADM Features & Phases
- Data Security Standards
- Data Steward – Stewardship Activities
- Data Modeling – Metrics and Checklist
- How to Measure the Value of Data
- What is Content and Content Management?


