Explanation KSA NDMO PDP.3.2 P1
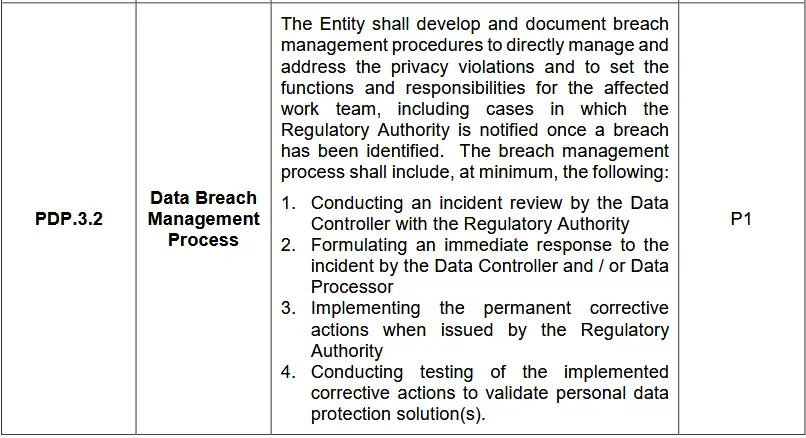
The Data Breach Management and Response Process outlines how an organization should handle and address data breaches. It details the steps for reviewing, responding to, and correcting breaches while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. It ensures a structured and compliant response to data breaches, mitigating potential risks and safeguarding personal data.
Key Points
- Incident Review: The Data Controller must review the breach with the Regulatory Authority.
- Immediate Response: The Data Controller and/or Data Processor should quickly address the breach.
- Corrective Actions: Implement permanent fixes as directed by the Regulatory Authority.
- Testing: Verify the effectiveness of corrective actions to ensure data protection.
General Activation Steps
- Incident Detection: Identify and report the breach to the Data Controller.
- Initial Assessment: Assess the breach’s impact and notify the Regulatory Authority if required.
- Immediate Response: Implement short-term measures to contain and mitigate the breach.
- Corrective Actions: Develop and apply long-term solutions as specified by the Regulatory Authority.
- Testing: Conduct tests to ensure the implemented actions effectively protect personal data.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of the breach, response actions, and tests.
Use Cases KSA NDMO PDP.3.2 P1
- Unauthorized Access: An employee’s credentials are used to access sensitive data without authorization.
- Data Exfiltration: Personal data is stolen or leaked due to a security vulnerability.
- System Compromise: A breach occurs due to a compromised system or software.
Dependencies
- Regulatory Guidelines: Compliance with regulations from the National Data Management Office (NDMO) and other relevant authorities.
- Incident Detection Tools: Systems for monitoring and detecting breaches (e.g., SIEM, IDS/IPS).
- Communication Channels: Methods for promptly notifying affected individuals and authorities.
- Corrective Action Tools: Solutions for addressing vulnerabilities and testing effectiveness.
Tools/Technologies KSA NDMO PDP.3.2 P1
- Incident Response Software: For tracking and managing the breach response (e.g., Splunk, ServiceNow).
- Data Encryption: Tools for securing data and preventing unauthorized access (e.g., Symantec, McAfee).
- Vulnerability Assessment Tools: For identifying and addressing system vulnerabilities (e.g., Nessus, Qualys).
- Testing Frameworks: Tools for validating the effectiveness of corrective actions (e.g., penetration testing tools).
For Your Further Reading:
- Data Strategy vs. Data Platform Strategy
- KSA PDPL (Personal Data Protection Law) – Initial Framework
- KSA PDPL – Consent Not Mandatory
- KSA PDPL – Article 5, Article 6, Article 7, Article 8, Article 9, & Article 10
- KSA NDMO – Data Catalog and Metadata
- KSA NDMO – Personal Data Protection – Initial Assessment
- KSA NDMO – Classification Process – Data Classification Metadata
- KSA NDMO – DG Artifacts Control – Data Management Issue Tracking Register
- KSA NDMO – Personal Data Protection – PDP Plan, & PDP Training, Data Breach Notification
- Enterprise Architecture Governance & TOGAF – Components
- Enterprise Architecture & Architecture Framework
- TOGAF – ADM (Architecture Development Method) vs. Enterprise Continuum
- TOGAF – Architecture Content Framework
- TOGAF – ADM Features & Phases
- Data Security Standards
- Data Steward – Stewardship Activities
- Data Modeling – Metrics and Checklist
- How to Measure the Value of Data
- What is Content and Content Management?


