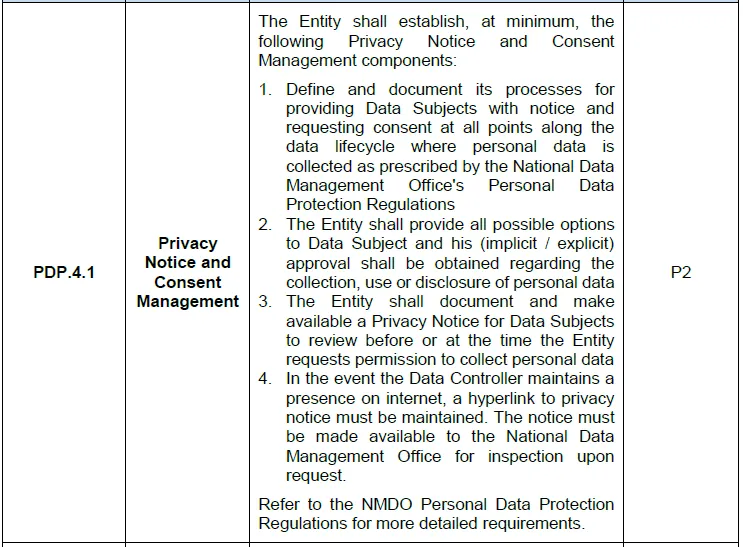
Abstract Of KSA NDMO PDP 4.1.P2
This paper outlines the essential components of Privacy Notice and Consent Management, as mandated by the National Data Management Office (NDMO) under its Personal Data Protection Regulations. Organizations must establish clear processes for obtaining consent and providing notice to Data Subjects at various points of data collection and processing. This paper provides a structured approach, covering key strategic points, activation steps, use cases, dependencies, tools, and technologies involved in achieving compliance with the NDMO guidelines. It also discusses the challenges and risks faced during implementation and offers practical recommendations for overcoming these obstacles.
Keywords
Privacy Notice, Consent Management, NDMO Regulations, Data Subjects, Personal Data Protection, Consent Lifecycle, Data Collection, Explicit Consent, Implicit Consent, Data Controller
Introduction Of KSA NDMO PDP 4.1.P2
In today’s data-driven world, the protection of personal data is a critical concern for individuals and organizations alike. The National Data Management Office (NDMO) of Saudi Arabia has introduced Personal Data Protection Regulations (PDPR) that dictate how entities must handle privacy notices and consent management. These regulations are designed to safeguard the rights of Data Subjects by ensuring transparency and control over personal data processing. This paper focuses on the privacy notice and consent management mechanisms that organizations must establish to align with the NDMO’s guidelines.
Explanation KSA NDMO PDP 4.1.P2
The NDMO requires organizations (Data Controllers) to provide clear, accessible information (Privacy Notices) to individuals (Data Subjects) before collecting their personal data. Furthermore, organizations must ensure that they obtain the Data Subject’s consent either explicitly (when the individual actively agrees) or implicitly (when consent is assumed based on actions like continued use of a service). At each step in the data lifecycle—whether data is being collected, used, or shared—the organization must maintain transparency and offer the Data Subject control over their personal data.
Key Strategic Points
- Transparency: Organizations must communicate clearly with Data Subjects about how their personal data is collected, processed, and shared.
- Consent: Data Subjects must have the option to grant or withhold consent, either explicitly or implicitly, for each purpose of data processing.
- Documentation: The entire consent process, including privacy notices, must be documented and available for review by both Data Subjects and regulatory authorities.
- Availability of Privacy Notice: Entities must ensure their Privacy Notice is accessible via hyperlinks, particularly if they maintain an online presence.
- Compliance with NDMO: Organizations must adhere to the specific consent and privacy notice requirements outlined in the NDMO’s Personal Data Protection Regulations.
General Activation Steps
- Define Consent Processes: Identify points along the data lifecycle where personal data collection occurs and develop procedures for issuing privacy notices and collecting consent.
- Create Privacy Notice: Draft a Privacy Notice that includes all required information, such as data collection purposes, Data Subject rights, and details on how the data will be processed and stored.
- Integrate Consent Mechanisms: Implement mechanisms (checkboxes, forms, etc.) that allow Data Subjects to provide explicit or implicit consent, ensuring these mechanisms are aligned with the NDMO guidelines.
- Documentation: Document the entire consent process, including logs of when and how consent was obtained, and ensure that these records are accessible.
- Ensure Accessibility: Maintain hyperlinks to the Privacy Notice on all digital platforms and ensure its availability to regulatory authorities on request.
Methodology
- Literature Review: Analyze NDMO’s PDPR and other relevant privacy frameworks like GDPR to establish best practices for privacy notice and consent management.
- Process Mapping: Develop flowcharts detailing how and when personal data is collected and the consent mechanisms involved at each step.
- Implementation: Build the technical infrastructure to support consent management, including user interfaces, tracking systems, and auditing mechanisms.
- Testing: Conduct pilot tests to ensure that privacy notices are visible and easily understandable, and that consent is properly recorded and stored.
Use Cases
- E-commerce Website: Before collecting customer information for targeted marketing, the website provides a clear Privacy Notice and a checkbox for explicit consent.
- Mobile Application: Upon installation, a mobile app presents the Privacy Notice and requires users to accept terms before collecting any data.
- Healthcare Service: A clinic informs patients about data collection via a Privacy Notice displayed on its website and requests consent for sharing medical records with third-party specialists.
Dependencies
- Legal Counsel: Organizations need legal guidance to ensure that privacy notices and consent forms comply with NDMO regulations.
- IT Infrastructure: Robust systems must be in place to manage, track, and store privacy notices and consent forms across all data collection points.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Cross-functional collaboration is required between legal, IT, and compliance teams to ensure that privacy notices and consent management are seamlessly integrated into business processes.
Tools and Technologies
- Consent Management Platforms (CMPs): Tools like OneTrust and TrustArc help organizations manage consent preferences across different platforms.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): WordPress and Drupal can be configured to display privacy notices and manage consent.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): These platforms allow for tracking customer data consent across multiple touchpoints in a seamless manner.
Challenges & Risks in KSA NDMO PDP 4.1.P2
- Ambiguity in Consent: Data Subjects may find it difficult to distinguish between implicit and explicit consent, leading to confusion and potential non-compliance.
- Data Subject Involvement: Ensuring that Data Subjects are aware of their rights and the implications of giving consent may require additional education efforts.
- Data Breaches: If privacy notices and consent data are not adequately secured, organizations risk exposing sensitive information.
- Continuous Monitoring: Ongoing compliance requires consistent monitoring of consent preferences, which may strain resources.
Conclusion
Adhering to the NDMO Personal Data Protection Regulations regarding privacy notices and consent management is not just a legal requirement but also a strategic need for building trust with Data Subjects. By defining processes, documenting consent, and ensuring transparency, organizations can not only comply with regulations but also enhance their data governance frameworks. Proper implementation of these components requires robust infrastructure, interdisciplinary collaboration, and continuous monitoring, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the challenges.
References
- NDMO – National Data Management Office, Personal Data Protection Regulations, 2024.
- KSA PDPL – Personal Data Protection Law, 2024.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), European Union, 2018.
- OneTrust, TrustArc – Consent Management Platforms, 2024.
For Your Further Reading:
- Big Data vs. Traditional Data, Data Warehousing, AI, and Beyond
- Big Data Security, Privacy, and Protection
- Data Strategy vs. Data Platform Strategy
- ABAC – Attribute-Based Access Control
- Consequences of Personal Data Breaches
- KSA PDPL (Personal Data Protection Law) – Initial Framework
- KSA PDPL – Consent Not Mandatory
- KSA PDPL Article 4, Article 5, Article 6, Article 7, Article 8, Article 9, & Article 10
- KSA PDPL Article 11, Article 12 & Article 13
- KSA NDMO – Data Catalog and Metadata
- KSA NDMO – Personal Data Protection – Initial Assessment
- KSA NDMO – DG Artifacts Control – Data Management Issue Tracking Register
- KSA NDMO – Personal Data Protection – PDP Plan, & PDP Training, Data Breach Notification
- KSA NDMO – Classification Process, & Data Breach Management
- Enterprise Architecture Governance & TOGAF – Components
- Enterprise Architecture & Architecture Framework
- TOGAF – ADM (Architecture Development Method) vs. Enterprise Continuum
- TOGAF – Architecture Content Framework
- TOGAF – ADM Features & Phases
- Data Security Standards
- Data Steward – Stewardship Activities
- Data Modeling – Metrics and Checklist
- How to Measure the Value of Data
- What is Content and Content Management?

