Plant and Animal cells are eukaryotic cells and can be differentiated as,
- Animal Cells: A specific kind of eukaryotic cell known as an animal cell lacks a cell wall and is made up of a genuine, membrane-bound nucleus in addition to other cellular organelles.
- Plant Cells: Eukaryotic cells with a genuine nucleus and specialized organelles that perform certain activities.
Comparison Between Plant And Animal Cells
- Eukaryotic cells, including those in plants and animals, have membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria.
- However, because they serve different purposes, animal and plant cells do not appear exactly alike or contain all of the same organelles. For instance, plants need chloroplasts to perform photosynthesis, whereas animal cells do not.
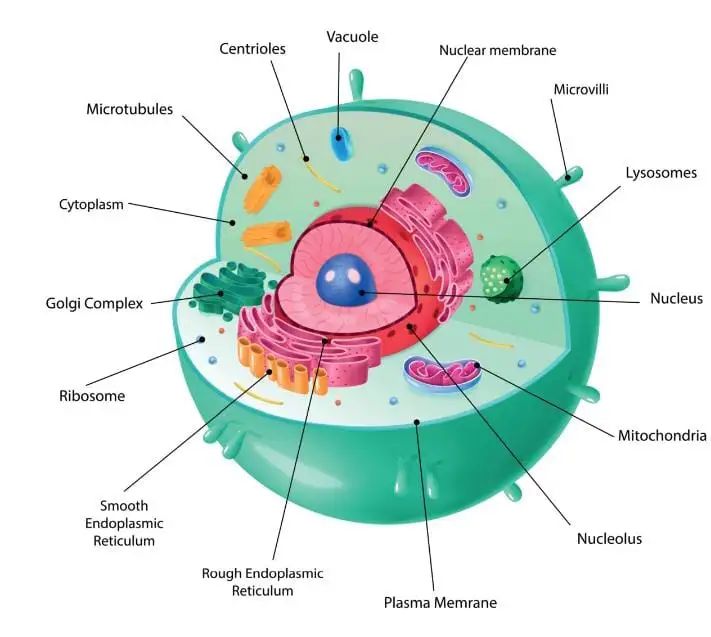
- While mitochondria are found in both plant and animal cells, chloroplasts are solely found in plant cells. Plants must produce their own sugar from sunlight since they cannot obtain it from food. The chloroplast is where the process of photosynthesis takes place.
- The mitochondria then break down the sugar after it is created in order to produce energy for the cell. Animals only need mitochondria since they obtain their sugar from the food they consume, not chloroplasts.
- Vacuoles are found in both cells. A plant cell has a big, single vacuole that serves as storage space and helps keep the cell in shape. Animal cells, on the other hand, have numerous, smaller vacuoles.
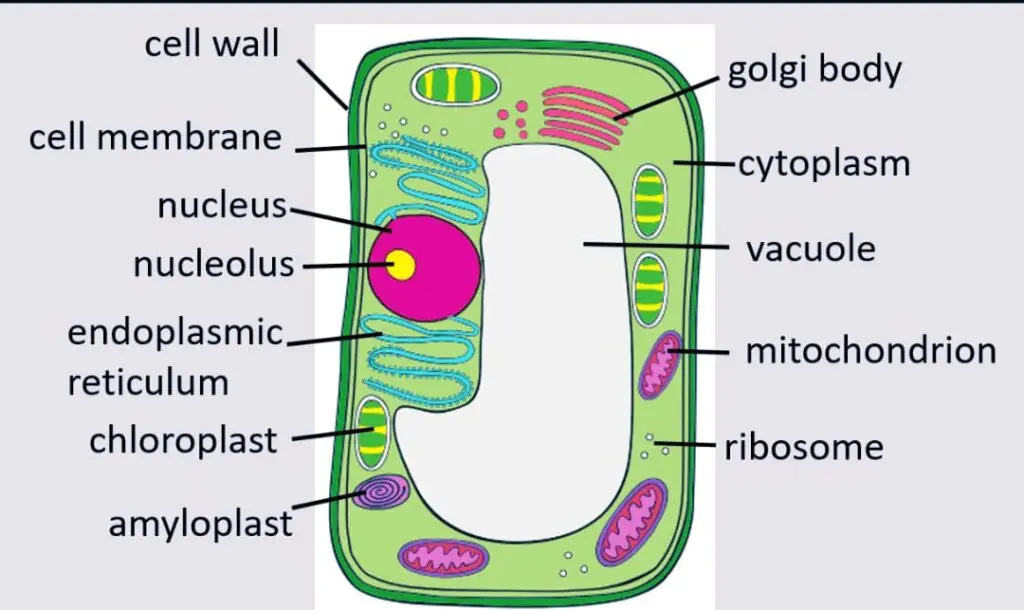
- Both a cell wall and a cell membrane are present in plant cells. In plants, the cell membrane is encased by the cell wall. The rectangular shape of the plant cell is a result of this. Animal cells lack a cell wall and only have a cell membrane.
- Membrane-bound organelles, including the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, the nucleus, the Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, and lysosomes, are present in both plant and animal cells.
- Additionally, they share membranes with cytoskeletal components and cytosol, for example. Additionally, a plant cell may be bigger than an animal cell.
- Animal cells typically range in size from 10 to 30 micrometers, while plant cells typically range in size from 10 to 100 micrometers.
Also Read About:

