Types of Plant Tissues and Their Functions
Plant tissues are multicellular eukaryotes that have tissue systems made up of different cell types that perform specific functions. These plant tissues consist of similar cells, each serving a specific purpose. When tissue types combine, they form organs, with each organ specialized for a particular function.
They are divided on the basis of their ability:
- Meristematic tissue.
- Permanent tissue.
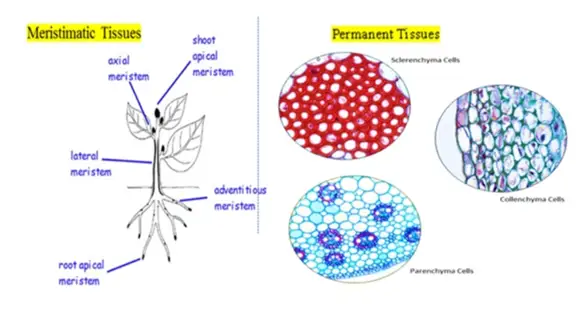
Meristematic Plant Tissues:
Made up of cells with the ability to divide. These tissues consist of small, cuboidal, densely packed cells that divide to form new ones. As they mature, these tissues can stretch, enlarge, and differentiate into other types of tissues.
Types of Meristematic tissue include;
Apical Meristem
These are located at the tips of the roots and shoots and contribute to the plant’s ability to grow taller. Different cell divisions aid in cellular enlargement and the growth of the cells in the roots and shoots.
Intercalary Meristem of Plant Tissues
These contribute to the internodes lengthening. The intercalary meristem is located in the leaves and internodes, contributing to the plant’s height as part of the apical meristem.
Lateral Meristem
It is located on the lateral side of the stems and roots. The plant becomes thicker as a result. The two lateral meristems are the vascular cambium and the cork cambium.
Permanent Tissues:
Derived from meristematic tissues and have lost their ability to divide. These are further divided into two types;
Simple Permanent Tissues
These also go by the name of homogeneous tissues. They consist of just one kind of cell, typically sharing the same origin, makeup, and purpose.
Complex Permanent Tissues
Heterogeneous, or made up of various cell types, are complex permanent tissues. All types of cells behave as one cohesive unit in these tissues, which serve as conducting tissues. These tissues are also known as vascular tissues because they are made up of vascular bundles.
Also Read About:

