What is RDM – Reference Data Management
Reference Data is any data used to characterize or classify other data, or to relate data to information.
Reference Data Management entails control and maintenance of defined domain values, definitions, and the relationships within and across domain values.
Goal of Reference Data Management
The goal of Reference Data Management is to ensure values are accurate, consistent and current across different functions and that the data is accessible to the organization. Like other data, Reference Data requires Metadata. An important Metadata attribute for Reference Data includes its source. For example, the governing body for industry standard Reference Data.
Use Cases and Flexibility of Reference Data
Reference Data may be stored in different ways to meet the different needs. For example, data integration (e.g., data mappings for standardization or data quality checks), or other application functionality (e.g., synonym rings to enable search and discovery). It may also have device specific user interface considerations (e.g., multiple languages).
Common Storage Techniques
- Code Tables in Relational Databases, linked via foreign keys to other tables to maintain referential integrity functions within the database management system
- Reference Data Management Systems that maintain business entities, allowed, future-state, or deprecated values, and term mapping rules to support broader application and data integration use
- Object Attribute Specific Metadata to specify permissible values with a focus on API or user interface access
Examples and Complexity of Reference Data
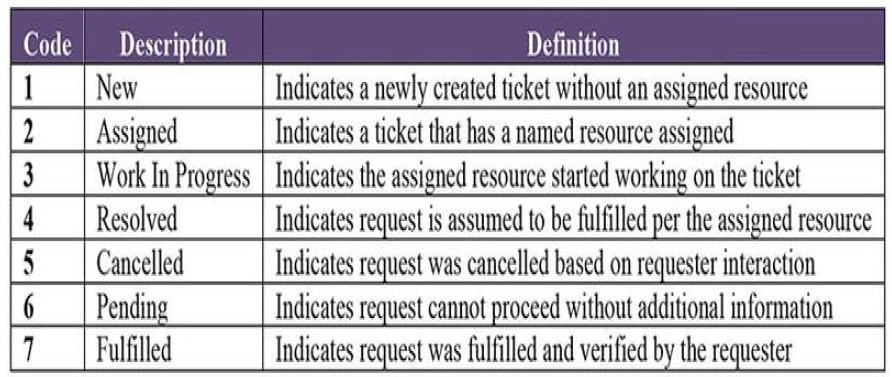
The most basic Reference Data consists of codes and descriptions, but some Reference Data can be more complex and incorporate mappings and hierarchies. Reference Data exists in virtually every data store. Classifications and categories may include status or types (e.g., Order Status: New, In Progress, Closed, Cancelled). External information may include geographic or standards information (e.g., Country Code: DE, US, TR).
Table of Reference Data Example