Tissues are collections of cells that share a similar form and function.
Between cells and organ systems, they provide a cellular organizational level. The body combines functional tissue groups to form organs.
Scientists categorize animal tissues into four types:
- Connective Tissue
- Muscle Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
- Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
- They consist of tissues made up of cells separated by an extracellular matrix, a non-living substance.
- The various organs are given shape by this tissue, which also helps to keep them in place. Blood, bone, tendon, adipose, and ligament are a few examples.
- Three different varieties of connective tissue exist: Fluid connective tissue, Fibrous connective tissue, and Skeletal connective tissue.
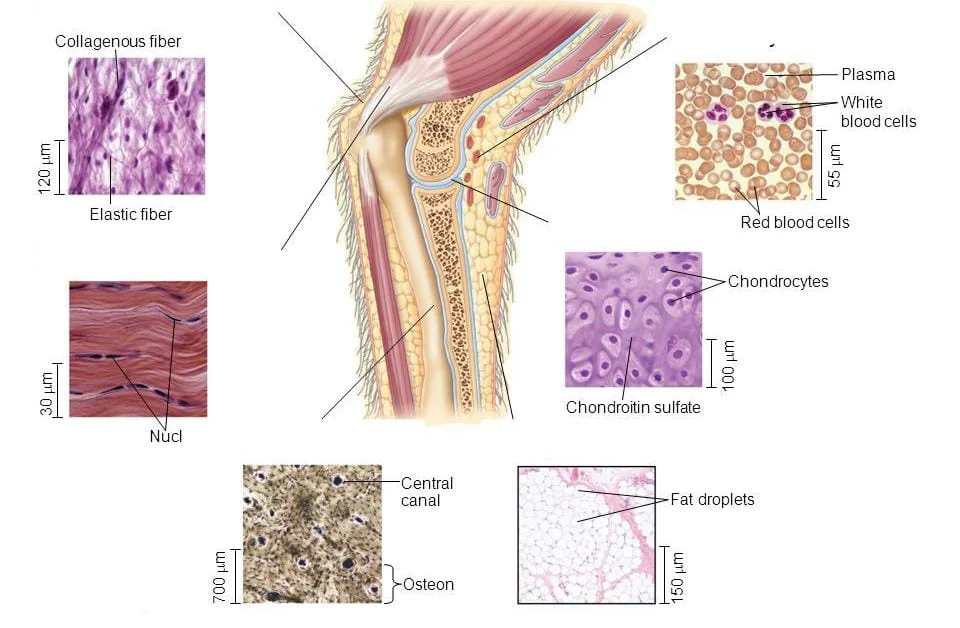
These are the bodily functions of connective tissue:
- Insulating.
- provide support and aid in tying the organs together.
- It defends against pathogen incursions by phagocytic activity.
- Gives the body shape, protects body heat, and stores energy.
- It moves water, nutrients, minerals, hormones, gases, and wastes throughout the body.
Muscle Tissue
- They create force and motion, whether for locomotion or movements within internal organs.
- Muscle tissue comes in three varieties:
- Skeletal muscles are usually connected to bones.
- There is cardiac muscle in the heart.
- They can be found in the interior organ walls and are known as visceral or smooth muscle.
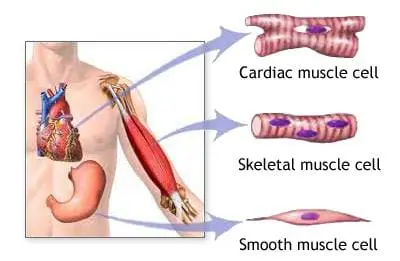
The body’s muscles serve the following purposes:
- Aids in maintaining a posture of uprightness.
- Aids in the constriction of blood vessels and organs.
- Both purposeful and involuntary movements are involved.
- Involved in blood pumping and controlling blood flow in arteries.
- Automatically drives the flow of air into and out of our bodies, controlling respiration.
Nervous Tissues
- They make up the majority of the brain and spinal cord’s tissue components in the central nervous system.
- Neural tissue in the peripheral nervous system forms the cranial and spinal nerves.
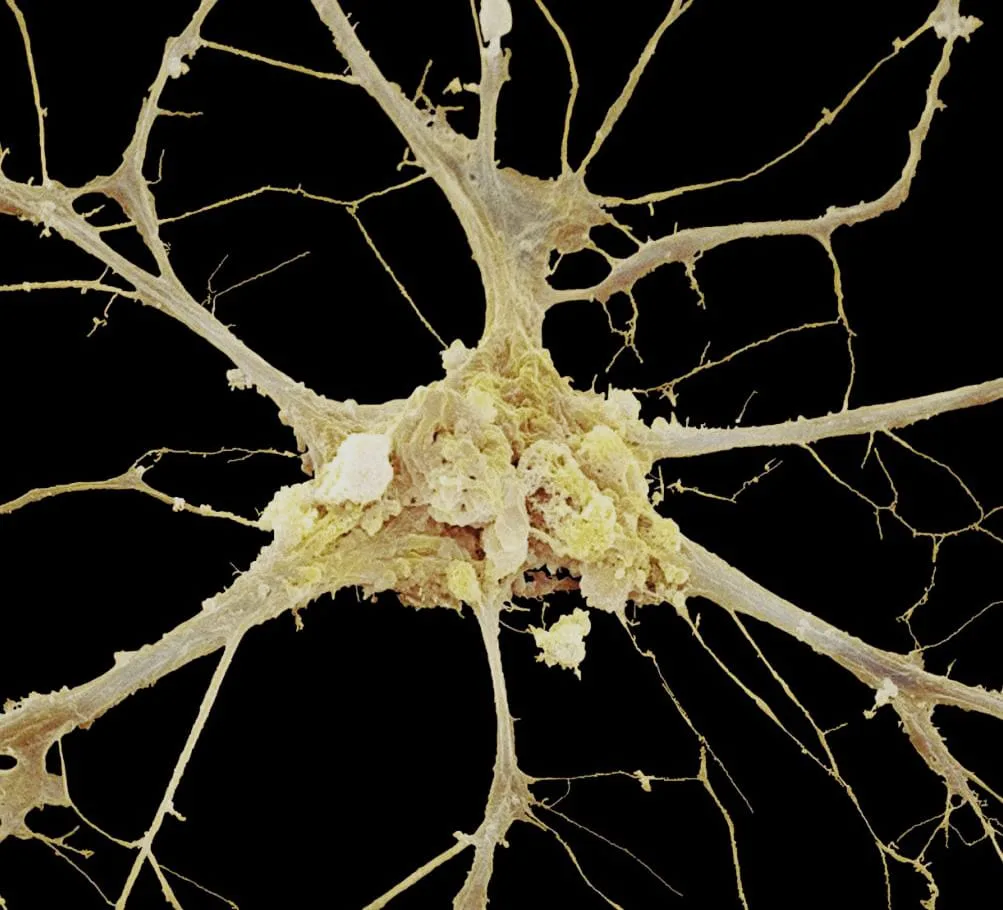
The body’s nervous system serves the following purposes:
- Reaction to a stimulus
- Information is stimulated and transmitted inside the body.
- It has a tremendous impact on emotions, memory, and thought.
- Keeps things stable and fosters environmental awareness.
- Nervous tissue controls and coordinates numerous metabolic processes.
Epithelial Tissues
- The same cells that line organ surfaces also form them, covering outer surfaces like the skin, reproductive system, airways, and digestive tract lining.
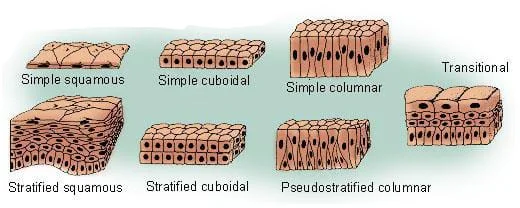
This tissue serves a wide range of purposes, such as:
- Play a crucial part in the reception of sensory information, excretion, filtration, and other metabolic processes.
- Give the underlying cells and tissue strength and resistance mechanically.
- It participates in the filtration, diffusion, and secretion processes that move materials.
- Defend the internal organs from pathogens, toxins, physical damage, radiation, etc.
Also Read About:

