In chemistry, Mixtures are the materials in which two or more chemicals combine without undergoing a chemical reaction.
- Both the result and the chemical combination of the ingredients do not cause the result to lose its uniqueness.
- Chemical elements and compounds are mechanically blended or mixed to create mixtures, which are the ultimate result.

General Mixture Properties
Mixtures are composed of two or more different substances that have not been chemically mixed. The following is a list of mixture properties.
- Each of the components in a mixture retains its unique features.
- Component separation is simple to carry out.
- The components’ relative weights vary.
Samples of Combinations
- A combination of organic substances known as crude oil (mainly hydrocarbons)
- Seawater is a combination of different salts and water.
- A blend of colored dyes is called ink.
- Carbon, potassium nitrate, and Sulphur are the main ingredients in gunpowder.
Mixture characteristics
A mixture’s components do not always exist in the same proportions. The following discussion covers the many features of mixes.
- Even when there is no longer a chemical force binding the two or more substances together, they coexist, nonetheless.
- Either they are heterogeneous or they are homogeneous.
- The ratios of the chemicals fluctuate indefinitely.
- The characteristics of the mixture rely on the constituent parts.
- Physical techniques can be used to separate the mixture’s components.
- The characteristics of the ingredients determine the mixture’s melting and boiling points.
- Energy remains constant while a combination is forming.
- Mixtures can be created from any combination of solid, liquid, and gaseous forms of matter.
Types of mixtures
Homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures are the two basic categories of mixtures. The many combination kinds are covered below.
Heterogeneous Of Mixtures
A heterogeneous mixture is one that contains both salt and sand. In other words, the properties are not consistent across a heterogeneous mixture, which has varied properties and composition in different sections.
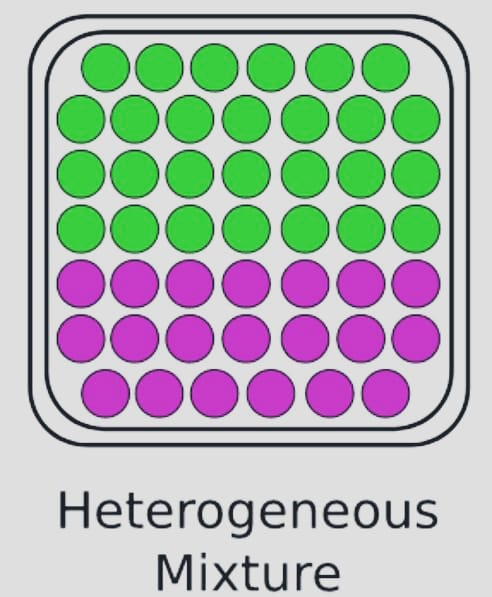
Examples: Air, oil, water, and other homogenous substances.
Homogenous Of The Mixtures
The most typical example of a homogenous mixture is sugar and water. Homogeneous mixtures are those that share the same characteristics and composition across their mass.
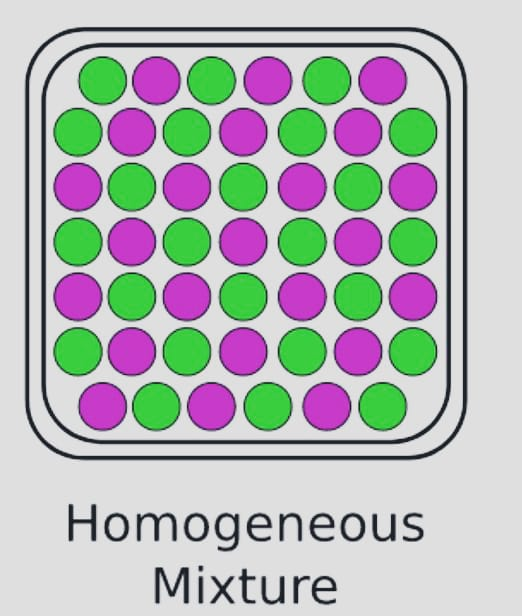
Examples: Metal alloys, salt and water, alcohol in water, and other substances.
For Further Reading:

